cuda 学习——julia 集计算
最近在学习 cuda ,正在看《 cuda by examples 》一书,感觉也是受益很多 之前在 B 站上也看了 NVIDA 的视频,结合起来还是很不错的
在这里记录一下学习的心得和笔记
关于 julia 集
关于 julia 集, julia 集合是一个在复平面上形成分形的点的集合 可以由下式得到
f(x)=x2+c
其中c是一个固定的复数
这样对于某一x,经过不停的迭代可以得到一序列
x,f(x),f2(x),f3(x)...
其中
fn+1(x)=x2+c
这样复平面内的点有的经过迭代后会发散到无穷,或始终处于某一范围之内并收敛于某一值。我们将使其不扩散的z值的集合称为朱利亚集合
我对Julia集的了解也并不深入(毕竟不是学数学的)不过这些知识对于计算来说也够用了
下面来慢慢分析
相关头文件下载
在分析代码之前我们需要先下载书中的头文件,我们在这个代码中用到了书中作者编写的部分头文件,下载链接为CUDA BY EXAMPLE
这是书的源代码,下载下来之后将common文件夹内需要的头文件其放到适合的位置,到时候include进来就好了
cuda 计算
julia函数
我们最终要的任务是计算上问的函数并判断是否收敛,对复平面内的每个点都要进行相同的运算,由于每个点的计算都是独立的,这就非常适合使用GPU进行并行计算.
代码也十分简单易于理解,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| __device__ int julia(int x, int y) {
const float scale = 1.5;
float jx = scale * (float)(DIM / 2 - x) / (DIM / 2);
float jy = scale * (float)(DIM / 2 - y) / (DIM / 2);
cuComplex c(-0.8, 0.156);
cuComplex a(jx, jy);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i<200; i++) {
a = a * a + c;
if (a.magnitude2() > 1000)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
|
首先我们把所有的点映射到-1到1的范围内,在这里要强制类型转换因为除法前后的都是整数所以如果不转换出来的结果全是0或者1,我当时就犯了这个错误导致出来的结果很迷,还debug了半天。
之后我们规定复数c和当前点,进行运算,若发散,返回0,不发散返回1,用于以后的运算
核函数kernel
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| __global__ void kernel(unsigned char *ptr) {
int x = blockIdx.x;
int y = blockIdx.y;
int offset = x + y * gridDim.x;
int juliaValue = julia(x, y);
ptr[offset * 4 + 0] = 255 * juliaValue;
ptr[offset * 4 + 1] = 0;
ptr[offset * 4 + 2] = 0;
ptr[offset * 4 + 3] = 255;
}
|
首先获得像素坐标,若不发散则设为红色,否则设为黑色
至于主函数则十分简单,创建矩阵分配内存,显示图片等正常操作
具体见下方代码
最后附上全部的代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
| #include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include "../common/book.h"
#include "../common/cpu_bitmap.h"
#define DIM 500
struct cuComplex {
float r;
float i;
__device__ cuComplex(float a, float b) : r(a), i(b) {}
__device__ float magnitude2(void) {
return r * r + i * i;
}
__device__ cuComplex operator*(const cuComplex& a) {
return cuComplex(r*a.r - i*a.i, i*a.r + r*a.i);
}
__device__ cuComplex operator+(const cuComplex& a) {
return cuComplex(r + a.r, i + a.i);
}
};
__device__ int julia(int x, int y) {
const float scale = 1.5;
float jx = scale * (float)(DIM / 2 - x) / (DIM / 2);
float jy = scale * (float)(DIM / 2 - y) / (DIM / 2);
cuComplex c(-0.8, 0.156);
cuComplex a(jx, jy);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i<200; i++) {
a = a * a + c;
if (a.magnitude2() > 1000)
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
__global__ void kernel(unsigned char *ptr) {
int x = blockIdx.x;
int y = blockIdx.y;
int offset = x + y * gridDim.x;
int juliaValue = julia(x, y);
ptr[offset * 4 + 0] = 255 * juliaValue;
ptr[offset * 4 + 1] = 0;
ptr[offset * 4 + 2] = 0;
ptr[offset * 4 + 3] = 255;
}
int main(void) {
CPUBitmap bitmap(DIM, DIM);
unsigned char *dev_bitmap;
HANDLE_ERROR(cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_bitmap, bitmap.image_size()));
dim3 grid(DIM, DIM);
kernel << <grid, 1 >> >(dev_bitmap);
将计算结果传输会host内存
HANDLE_ERROR(cudaMemcpy(bitmap.get_ptr(), dev_bitmap,
bitmap.image_size(),
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost));
bitmap.display_and_exit();
HANDLE_ERROR(cudaFree(dev_bitmap));
}
|
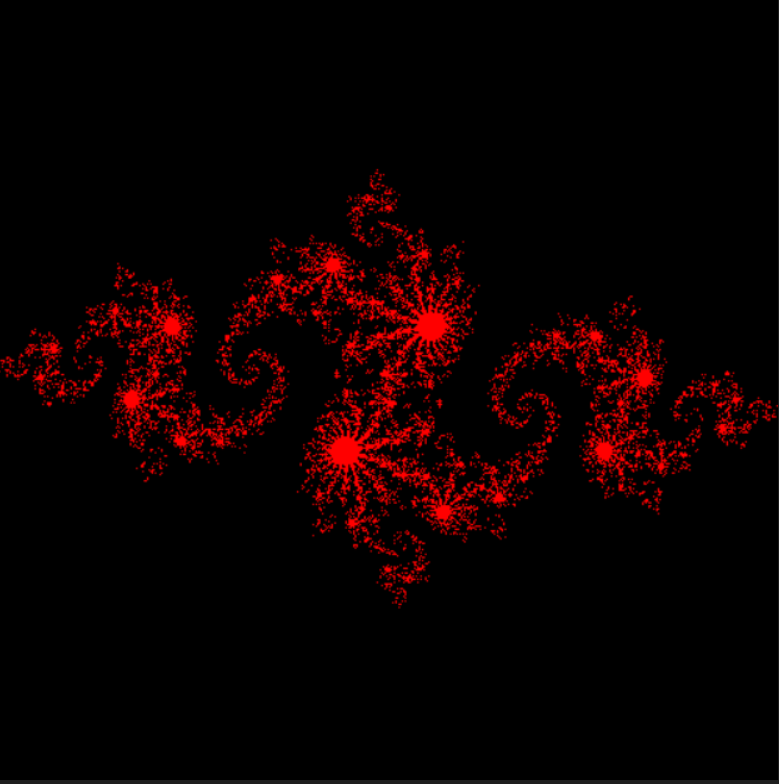
结果
常见错误
找不到glut64.lib 或glut32.lib
遇到此问题时,将在第一步时下载的源码中lib/glut64.lib和lib/glut32.lib复制进入**C:\Program Files**\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v9.2\lib文件夹下对应的文件夹中,如果是x64的就放入x64文件夹中,32位的就放入Win32文件夹中,路径中加粗的部分为cuda的安装位置
或者百度搜索也会有很多其他解决方案







